The Straightening of Titanium Tubes
Titanium tubes, either welded or seamless, made to ASME SB-338/ ASTM B338, are widely used for heat exchanger and condenser applications. These tubes are generally furnished in small diameter and thin wall. In spite of great advances in manufacturing processes, no titanium tube can be produced perfectly straight and round initially. The straightening process shall be introduced to reduce ovality as well as improve straightness.

A Six-rolls straightener for titanium tube straightening
Generally, the titanium tubes are straightened by a combination process which includes bend straightening and oval-flattening straightening processes on a six-rolls straightener.
Bend Straightening Mechanism
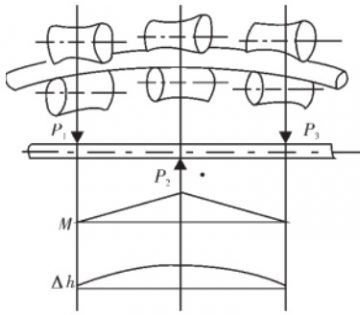
Stress/force analysis on bend straightening process.
As the titanium tube passes through a curved path caused by 3 pairs of rolls, the tube is fed helically relative to the rolls. As a result, the titanium tube is straightened by the cycling stresses exerted on the external surface in contact with the rolls. Bend straightening is the main straightening action for titanium tubes. However, its disadvantage is obvious: two lengths of both ends of the tube can not be straightened due to the feeding characteristics.
Oval-Flattening Straightening Mechanism
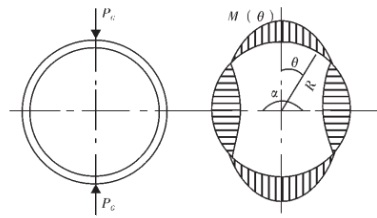
Stress/ force analysis on oval-flattening straightening process.
In order to straighten the titanium tube completely, a oval-flattening straightening mechanism shall be conducted also on the six-rolls straightener. When the tube is fed through a pair of rolls, the gap between them can be adjusted to a distance that is slightly smaller than the outside diameter of the tube. If the pressure caused by this dimensional difference is large enough, the tube section is flattened to oval shape temporarily under the cycling stress causing straightening of the titanium tube. Some of the ovality may also be removed.
