Analysis on Ductility and Fracture of Monel 400
The high-temperature tension tests for Monel 400 specimens were conducted at 600°C, 700°C, 800°C, 900°C, 1000°C, and 1100°C. The elongation, reduction of area, and fracture surface at elevated temperatures are illustrated respectively.
Elongation & Reduction of Area Chart for Monel 400
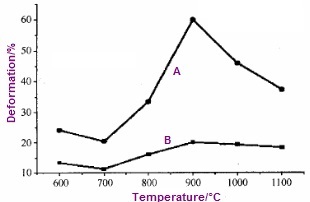
Elongation & Reduction of Area chart for Monel 400 at elevated temperatures. A-reduction of area curve; B-elongation curve.
When the test temperature increases from 600°C to 700°C, the elongation value decreases from 13.26% to 11.22% while the reduction of area decreases from 24.26% to 20.47%. The ductility of Monel 400 decreases as the temperature goes up in this range. As the test temperature increases from 700°C to 900°C, the elongation value increases from 11.22% to 20.05% while the reduction of area increases from 20.47% to 60.05%. The ductility of Monel 400 increases as the temperature goes up in this range. As the temperature rises up from 900°C to 1100°C, the ductility decreases again. Monel Alloy 400 exhibits hot brittleness between 600°C and 800°C.
The Fracture of Monel 400 Specimens at Elevated Temperatures
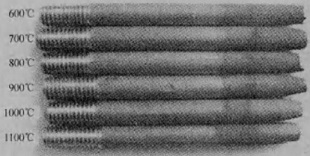
Macrostructure of Monel 400 after fracture at elevated temperatures.
From the macrostructure after fracture, obvious necking of Monel 400 is observed at temperatures between 800°C to 1000°C and it achieves maximum at 900°C. It proves that Monel 400 has improved ductility at this temperature range.
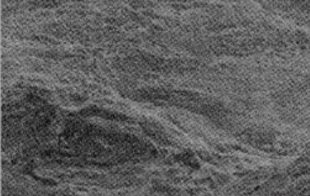
Microstructure of fracture surface of Monel 400 at 600°C by SEM. Picture A
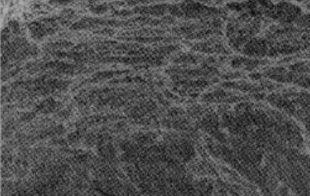
Microstructure of fracture surface of Monel 400 at 700°C by SEM. Picture B

Microstructure of fracture surface of Monel 400 at 800°C by SEM. Picture C.
The microstructure of the fracture surface of Monel 400 at 600°C, 700°C and 800°C are attained by SEM method. Both pictures A and B exhibit quasi-cleavage fracture in river pattern. It indicates the brittle fracture. Some dimples are observed in Picture C except for cleavage fracture. It proves that the ductility shall be improved at 800°C.
