Corrosion Resistance of Hastelloy C-276 to Hydrochloric Acid
Hastelloy C-276 has outstanding resistance to hydrochloric acid. It is resistant to all concentrations of hydrochloric acid at room temperature, and can be employed successfully up to about 120°F [49°C].
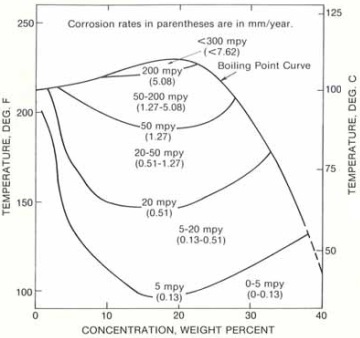
Diagram A: isocorrosion diagram for Hastelloy C-276 in hydrochloric acid.
Diagram A illustrates the corrosion resistance of Hastelloy C-276 in hydrochloric acid. There are 4 lines that indicates specific corrosion rate at corresponding temperature and acid concentration. The extra line is the boiling point curve of hydrochloric acid. Take line-“5 mpy” for example, it represents the combination of HCl acid concentration and temperature at which a corrosion rate 5 mpy (0.13 mm/year) is expected. Below the line, the corrosion rate of 0~5 mpy (0~0.13 mm/year) is expected. Between line-“5 mpy” and line-“20 mpy”, a corrosion rate of 5~20 mpy (0.13~0.51 mm/year) may be expected.
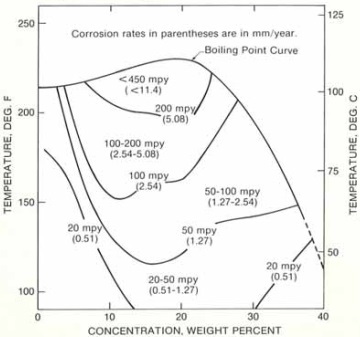
Diagram B: isocorrosion diagram for Hastelloy C-276 in HCl acid purged with oxygen.
Diagram B illustrates the corrosion resistance of Hastelloy C-276 to hydrochloric acids that are purged with oxygen. Oxygen dissolved in HCl solution may drastically accelerate the corrosion attack since it is not a strong enough oxidizer to passivate Alloy C-276.

Diagram C: isocorrosion diagram for Hastelloy C-276 in HCl solution purged with nitrogen.
Diagram C illustrates the corrosion resistance of Hastelloy C-276 to hydrochloric acid purged with nitrogen. Nitrogen dissolved in HCl solution may effectively inhibit the corrosion attack to some extent. Thus, the corrosion rate will decrease comparatively under the same condition.
